What do catastrophic health plans cover?
Catastrophic insurance coverage helps you pay for unexpected emergency medical costs that could otherwise amount to medical bills you couldn’t pay. It also covers essential health benefits, including preventive services like health screenings, most vaccinations, your annual check-up, and certain forms of birth control.
What don’t catastrophic health plans cover?
Your catastrophic health plan doesn’t cover emergency care until you’ve met your deductible. And there may be certain limits on preventive care and number of covered visits to a Primary Care Provider (PCP), depending on the plan.
It’s important that you understand what is and is not covered by your particular plan.
What kind of medical care is covered by catastrophic health insurance?
Once you meet your plan deductible, catastrophic coverage would pay for accidents, unexpected injuries, sudden emergency illnesses, etc. These plans also provide 100% coverage for certain preventive care services—annual check-up, flu shot, certain types of routine screenings, and more.
Most catastrophic plans also cover you for at least three visits to a PCP.
Do I qualify for catastrophic insurance?
You must either be under 30, or qualify for a hardship exemption. Usually, an exemption means that you can’t afford health care insurance because you’ve recently been homeless, declared bankruptcy, or meet other qualifying criteria.
How do I qualify for an exemption so that I can get catastrophic health coverage?
There are two main types of exemptions that would help you qualify for catastrophic insurance—personal hardship and affordability exemptions. You could qualify for either exemption depending on the details of your specific situation.
Some common hardship qualifications include:
- Homelessness
- Bankruptcy
- Domestic violence
- Death of a close relative
- Utility services being shut off
- Eviction
- Home foreclosure
- A fire, or a natural- or human-caused disaster that results in substantial property damage
There are also affordability exemptions. This means that your income is not enough to be able to afford regular health care coverage. If you qualify for an exemption, you would claim it on your annual tax return and get money back.
How do I apply for an exemption?
To apply, you must fill out an application and submit it to the Exchange. You can find forms on Healthcare.gov. You’ll receive a notification in the mail from the Exchange letting you know if you qualify for the exemption or not.
If your priority is finding insurance with a low monthly fee, catastrophic insurance may be right for you. To qualify for catastrophic insurance, you must be under 30, or, qualify for a hardship exemption. The application is approved or denied based on the details of your specific circumstances.
If I qualify for an exemption, can I get catastrophic health insurance?
If you are approved for either a hardship or affordability exemption, it means you may then get a catastrophic health insurance plan, if you choose.
Catastrophic health plans can help protect you from high emergency medical costs, while also covering some essential health benefits like an annual check-up, certain preventive services, and at least three primary care visits before you have met your deductible. However, if you anticipate costs associated with managing a chronic health condition, you may save more with another type of health plan.
How to claim emergency health insurance without any complications?
When a medical emergency occurs, the first thing you need to do is not panic. Contact the nearest hospital with emergency care, book an ambulance and transport your patient there. Once your patient is under the medical supervision of a registered practitioner, you can fret about the claim.
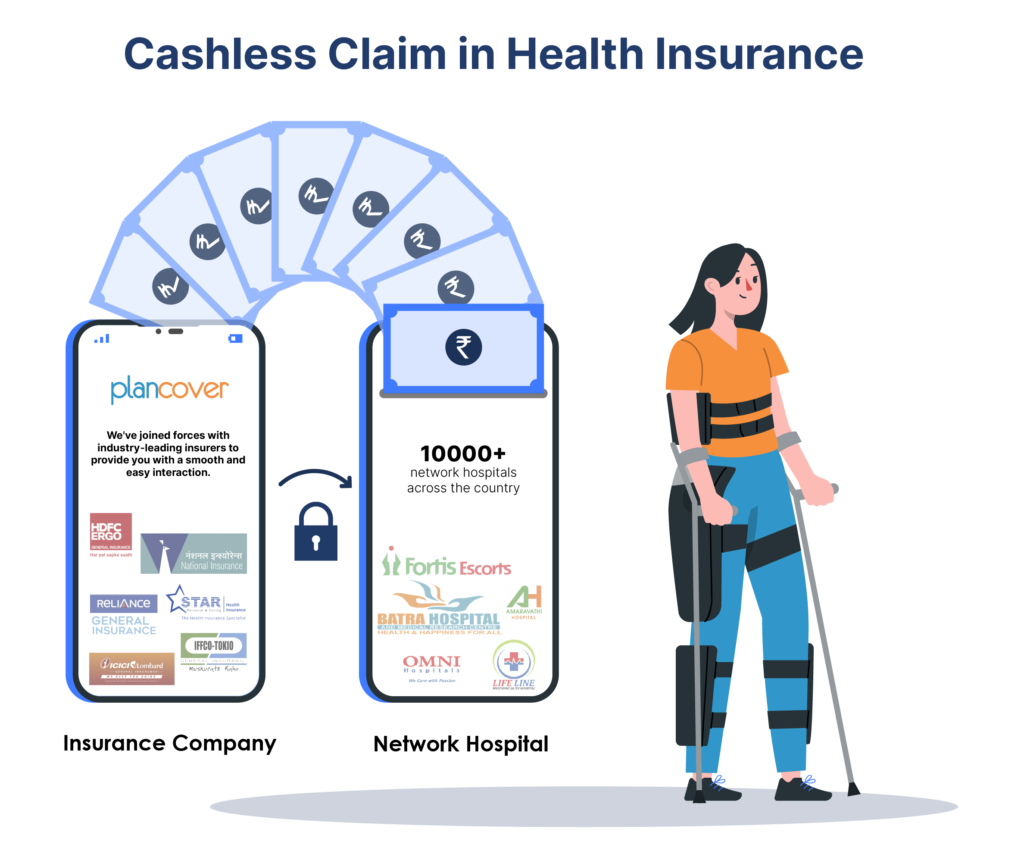
Before starting an emergency health insurance claim, ensure you are aware of the network hospitals where you can take your patient without having to fret about the medical bills. If the hospital of your choice is empanelled with your insurer, all you need to do is provide a copy of your health card or policy document and the patient’s KYC documents, i.e. identity proof (PAN Card will do) to admit him in the emergency ward.
Ideally, for planned hospitalisation, you need to inform your insurer at least 3-4 days before hospitalisation to authorise a cashless claim. However, for emergency hospitalisation, you can do so within 24 hours of hospitalisation. You need to submit the duly filled pre-authorisation form along with the insured person’s identity proof and health card of your valid health insurance policy at the TPA or insurance desk of the hospital. Once the hospital receives the initial approval from the insurer, you can continue the treatment of your patient in a cashless manner.
At the time of discharge, the hospital would send the final bill to the insurer for approval. Most parts of the bill should be settled directly by the insurer, but the portion that is not payable, such as consumables, co-payment, if any, etc., must be paid by you at discharge.
However, if you opt for a non-network hospital, you need to make a payment upfront and then provide all original bills and receipts to the insurer to file a reimbursement claim. However, remember to inform your insurer about the hospitalisation within 7-15 days of admission as per the policy’s timelines mentioned.
How to keep prepared for a possible medical emergency?
Here are some tips to keep yourself and your family prepared for a possible medical emergency:
1. Know the details about the health insurance policy.
Keep the health cards handy. Know the insurer’s toll-free number and email id so that you inform the insurer of the possible health insurance claim and register the same.
2. Network of hospitals:
Keep yourself and your family aware of the updated list of the network of hospitals with your insurer, wherein you can avail of a cashless hospitalisation without having to pay anything upfront. This is a piece of essential information, and make sure all members of the family are aware so that they are fully equipped to handle any medical emergency without your assistance.
3. Medical records:
Keep a record or an archive of your family’s medical history, current and past ailments, and the regular medicines that you or anyone in your family takes so that it can be informed to the doctor at the hospital in case of emergency hospitalisation. If only the concerned person is aware, others may not be able to provide accurate information to the doctor for correct diagnosis and treatment. So, having an online medical archive could come to your rescue.
Conclusion
Emergency health insurance claim is one of the most important reasons for availing of a health insurance plan. So, keeping yourself and your family updated about the process will not only help you ease the process but also give you the confidence to proceed with the claim without having to take help.
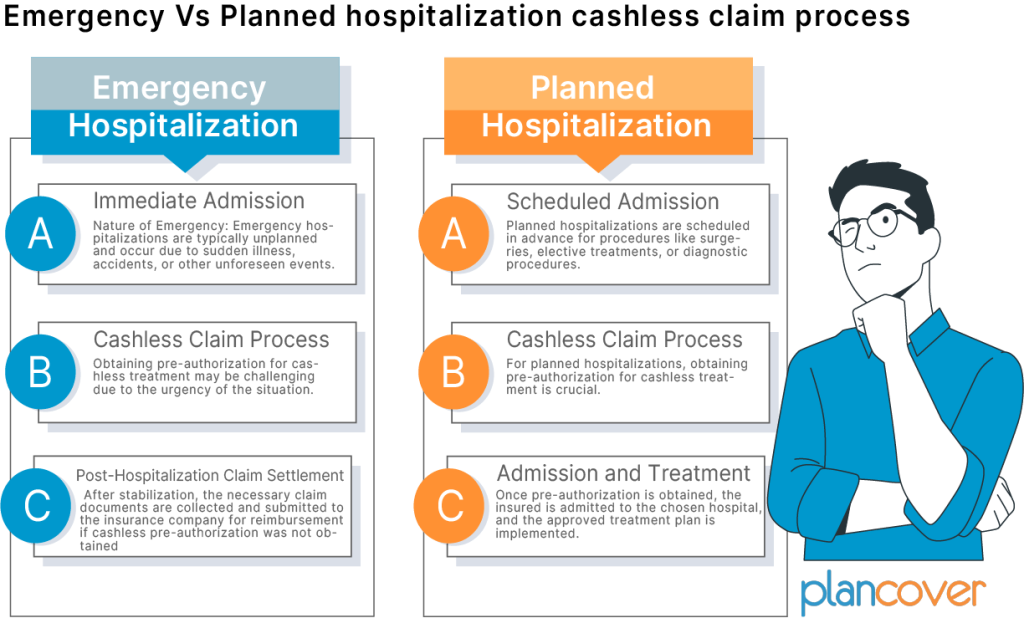
Emergency Vs Planned hospitalization cashless claim process
The cashless claim process in health insurance can differ between emergency and planned hospitalizations. Here’s an overview of the distinctions between these two scenarios:
Emergency Hospitalization:
Immediate Admission:
Nature of Emergency: Emergency hospitalizations are typically unplanned and occur due to sudden illness, accidents, or other unforeseen events.
Immediate Care: In emergency situations, the priority is to provide immediate medical care. The insured individual may be taken to the nearest hospital that can address the emergency.
Cashless Claim Process:
Pre-authorization Challenges: Obtaining pre-authorization for cashless treatment may be challenging due to the urgency of the situation. However, many insurance companies have provisions for post-authorization in emergencies.
Informing the Insurer: The insured or their family needs to inform the insurance company as soon as possible after hospitalization, providing details of the emergency.
Post-Hospitalization Claim Settlement:
Claim Documentation: After stabilization, the necessary claim documents are collected and submitted to the insurance company for reimbursement if cashless pre-authorization is not obtained.
Retroactive Authorization: In some cases, the insurance company may retroactively authorize cashless treatment, provided the emergency was genuine and the treatment was covered.
Planned Hospitalization:
Scheduled Admission:
Nature of Planned Hospitalization: Planned hospitalizations are scheduled in advance for procedures like surgeries, elective treatments, or diagnostic procedures.
Choice of Hospital: The insured has the opportunity to choose a network hospital for planned hospitalization, optimizing benefits.
Cashless Claim Process:
Pre-Authorization: For planned hospitalizations, obtaining pre-authorization for cashless treatment is crucial. The insured or the hospital initiates this process by submitting relevant documents to the insurance company.
Verification and Approval: The insurance company reviews the pre-authorization request, verifies policy coverage, and approves the treatment plan if it meets the policy terms.
Admission and Treatment:
Hospital Admission: Once pre-authorization is obtained, the insured is admitted to the chosen hospital, and the approved treatment plan is implemented.
Direct Settlement: The hospital bills are directly settled by the insurance company as per the pre-approved amount.
Post-Hospitalization:
Documentation: The insured may need to submit additional documents post-hospitalization, such as original bills, medical reports, and discharge summaries.
Reimbursement (if required): If there are any non-network expenses or if the insured opts for a hospital outside the network, reimbursement is processed based on the submitted documents.
In summary, while both emergency and planned hospitalizations may involve cashless claims, the process can vary based on the nature of the situation. Emergency hospitalizations focus on immediate care, and cashless approval may be obtained post-hospitalization. In contrast, planned hospitalizations require pre-authorization to ensure a smooth and direct settlement process. Insured individuals should be aware of the specific procedures outlined in their health insurance policy and communicate with the insurance company accordingly.
Pingback: Taking a Trip? Information About Travel Insurance You Should Know Before You Hit the Road - Unraveling the Digital World